Leave Your Message
In today’s world, efficient heating and cooling are essential for homes. Heat pumps are a popular solution for achieving this balance. According to Dr. Emily Renshaw, a renowned expert in HVAC systems, “Heat pumps offer one of the best ways to maintain temperature comfort while saving energy.”
The versatility of heat pumps makes them suitable for various climates. These systems can both heat and cool spaces, making them a year-round solution. However, selecting the right heat pump can be overwhelming. There are many factors to consider, including size, efficiency, and technology. Each option has its pros and cons that can impact overall performance.
Many homeowners may not know that installation quality affects efficiency. A poorly installed heat pump might not deliver expected results. It’s crucial to hire qualified professionals for installation. Choosing the right heat pump requires research and reflection. The options can be vast, and not all will suit every need. Evaluating your requirements is key in making the right choice.

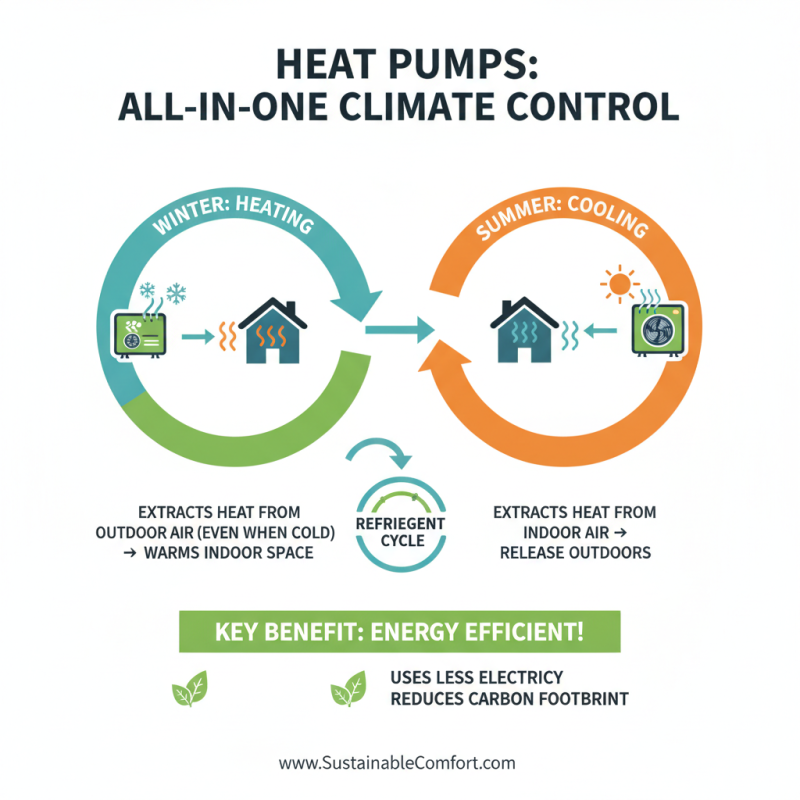
Heat pumps are versatile systems designed for both heating and cooling. They transfer heat from one location to another using refrigerant. A heat pump can extract warmth from the outside air, even in cold weather, and bring it indoors. This principle makes them energy efficient compared to traditional heating systems.
In cooling mode, heat pumps work in reverse. They pull warm air from inside your home and release it outside. This dual functionality makes them a preferred choice for many homeowners. However, their effectiveness can vary by region and temperature. Some systems struggle in extreme cold, leading to the need for supplemental heating. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance year-round. This can include cleaning filters and checking for refrigerant leaks.
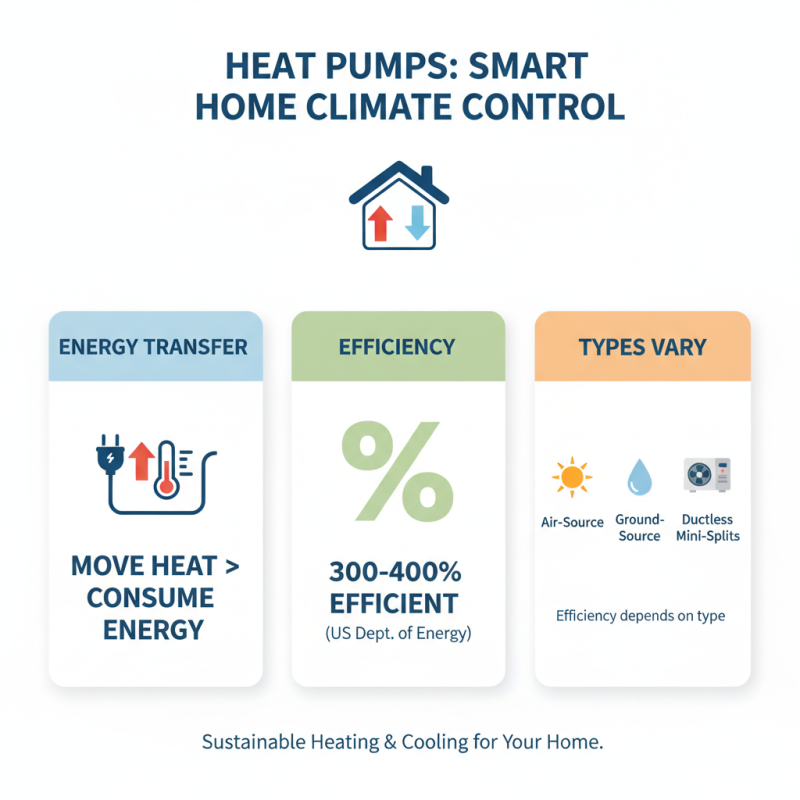
Heat pumps are an effective solution for heating and cooling homes. They use electricity to transfer heat, making them energy-efficient. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can be 300-400% efficient. This means they move more heat than the energy they consume. But this efficiency varies based on the type of heat pump used.
There are several types of heat pumps suitable for home applications. Air-source heat pumps are common. They absorb heat from the outside air. Ground-source, or geothermal, heat pumps utilize the constant temperature underground. These systems are more efficient but have higher upfront costs. A study by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy notes that geothermal systems can save homeowners up to 70% on heating costs. However, installation can be complex and disruptive.
Ductless mini-split heat pumps offer flexibility. They allow zoned heating and cooling. These units can be installed without ductwork. Although they provide comfort, they may require meticulous planning for optimal placement. The right choice often depends on specific home needs and local climate. While heat pumps are generally a smart investment, homeowners should weigh efficiency against installation challenges.
When selecting a heat pump, several factors demand careful consideration. Energy efficiency stands out as a primary concern. Reports indicate that heat pumps can operate at efficiencies over 300%. This means they can produce three times more energy than they consume. Choosing a model with a high energy efficiency ratio (EER) is crucial. It can lead to significant savings on utility bills.
Another key aspect to consider is climate suitability. Not all heat pumps perform well in extreme temperatures. Some systems lose efficiency when the temperature drops below freezing. In colder regions, look for models with a cold climate designation. They are designed to maintain performance in low temperatures, enhancing reliability.
Installation and maintenance also play vital roles in the heat pump's long-term efficiency. A poorly installed system can result in a 30% drop in efficiency, according to industry studies. Regular check-ups and timely maintenance can prevent costly repairs. Moreover, subsidy availability and installation costs may influence your choice. Evaluate upfront costs versus potential energy savings for a holistic view.
| Model | Heating Efficiency (HSPF) | Cooling Efficiency (SEER) | Noise Level (dB) | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 9.0 | 16 | 50 | $3,000 - $4,000 |
| Model B | 9.5 | 17 | 55 | $3,500 - $4,500 |
| Model C | 8.5 | 15 | 52 | $2,800 - $3,800 |
| Model D | 10.0 | 18 | 48 | $3,200 - $4,200 |
| Model E | 9.3 | 16.5 | 53 | $3,100 - $4,100 |
When choosing a heat pump, efficiency is key. The most efficient models can achieve a Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) of 20 or higher. This rating shows how much cooling a heat pump provides for each unit of electricity consumed. For heating, the Heating Season Performance Factor (HSPF) should ideally be above 10. Higher numbers indicate better efficiency.
To ensure optimal heat pump performance, regular maintenance is essential. Maintenance helps your system run efficiently and can extend its lifespan. Start by cleaning or replacing filters every month. Dirty filters restrict airflow and can lead to inefficiency. A simple task, yet many forget it.
Next, check the outdoor unit frequently. Keep it free of debris like leaves and branches. These obstructions can hinder performance. A clean unit absorbs heat effectively. Sometimes we neglect this routine, so reminders help.
Also, schedule professional inspections yearly. Technicians can find issues before they escalate. They check refrigerant levels and test the thermostat. It's an investment in your comfort. Remember, small oversights can lead to larger problems. Stay proactive for a cozy home year-round.