Leave Your Message
Choosing the right heat pump for your home can feel overwhelming. Experts like John Smith, an HVAC industry leader, emphasize, "The right heat pump can transform your living space's comfort." With many options available, it's crucial to consider several factors.
When selecting a heat pump, evaluate your home’s insulation. Poor insulation can lead to inefficiencies. Additionally, consider the size of your home. An oversized unit may cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy. One size does not fit all.
Budget is another element to reflect on. Upfront costs can be high, but energy savings are significant over time. However, cheaper models may lead to repairs. Take time to research brands and warranties. Mistakes can be costly. A well-informed decision will lead to lasting comfort in your home.
Choosing a heat pump for your home can be daunting. You'll need to consider various factors. The climate in your area is crucial. If it's consistently cold, you might need a high-capacity heat pump. However, in milder regions, a lower-capacity model may suffice. Also, consider the size of your home. A larger space requires more heating power.
Tips: Assess your insulation. Good insulation helps retain heat. It makes a difference in efficiency. This factor sometimes gets overlooked. Check your home’s layout too. Open floor plans may distribute heat better than multi-story homes. If you have lots of windows, some pumps may need additional support.
Another aspect is your energy source. Heat pumps can run on electricity or gas. Your access to these resources may affect your choice. Look at maintenance needs. Some units require more upkeep than others. This could be a long-term commitment.
Tips: Always read user reviews. They can reveal common issues. Also, consult professionals. They can provide insights based on experience. Don't rush this decision. Take your time to reflect on your specific needs.
When choosing a heat pump, understanding the types is crucial. Air-source heat pumps are popular. They draw heat from the air outside. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, they can be 50% more efficient than traditional heating systems. However, their performance drops in extremely cold weather. This can lead to increased energy usage.
Ground-source heat pumps, on the other hand, utilize the earth's stable temperature. They are often more efficient, providing heat even in frigid conditions. The Energy Saving Trust reports that ground source systems can reduce heating bills by up to 30%. Yet, installation costs are notably higher. Homeowners must weigh the long-term savings against initial investments.
Home climate and local conditions play a vital role in the decision. For instance, colder climates might benefit from ground-source systems. But, in milder areas, air-source options may suffice. Each type has its drawbacks. An informed choice is essential to maximize efficiency and comfort over time.
| Type of Heat Pump | Efficiency (COP) | Installation Cost Range | Maintenance Requirements | Lifespan | Ideal Climate Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Source Heat Pump | 3.0 - 4.0 | $3,500 - $8,000 | Regular cleaning and service every 1-2 years | 15 - 20 years | Mild climates, can work in cold but less efficiently |
| Ground Source Heat Pump | 4.0 - 5.0 | $10,000 - $25,000 | Less frequent maintenance; check-up every 3-5 years | 20 - 25 years | Wide range of climates, very efficient in extreme temperatures |
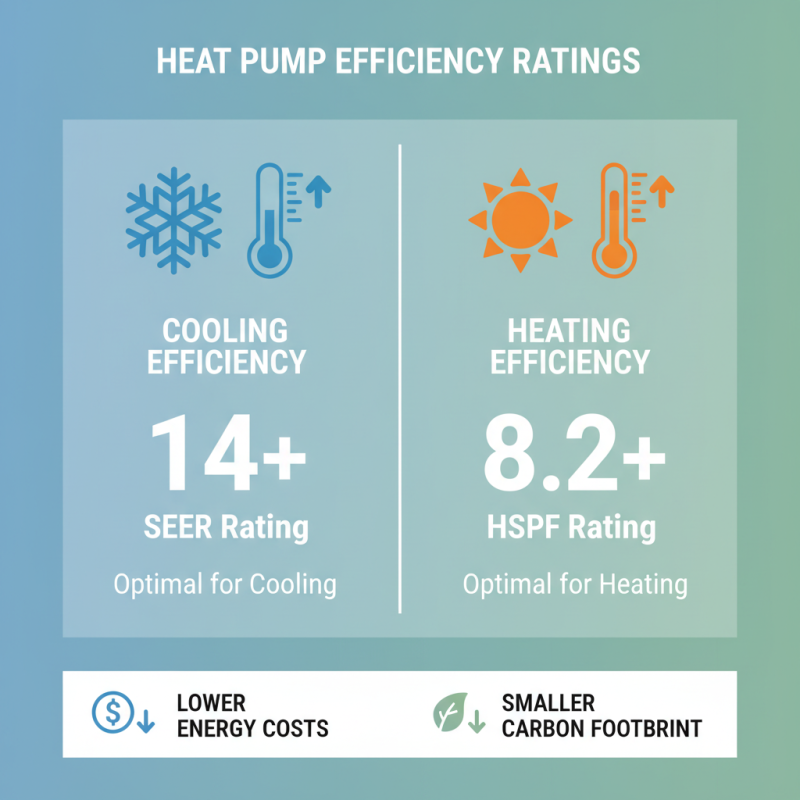
When selecting a heat pump, understanding efficiency ratings is essential. Two key metrics to consider are SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Season Performance Factor). The U.S. Department of Energy states that a SEER rating of 14 or higher is optimal for cooling efficiency. Similarly, an HSPF of 8.2 or greater indicates a high level of heating efficiency. Notably, higher ratings generally translate to reduced energy costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
Tips: Look for units with the highest SEER and HSPF ratings that fit your budget. A well-rated heat pump can provide significant savings. However, some models may be pricier upfront, which requires careful budgeting.
It's crucial to consider the home's climate. In colder regions, even a high HSPF might not yield satisfactory results. The performance can vary significantly based on insulation quality and local weather conditions. Evaluating these factors is as essential as the ratings themselves. A professional home energy assessment may offer useful insights.
Tips: Always assess your current insulation and energy needs before choosing a heat pump. Beware of potential mismatches between system capacity and your home's requirements.
Choosing the right heat pump is crucial for home comfort. One key factor is sizing, which relies heavily on BTU calculations. BTU, or British Thermal Unit, measures energy required to raise the temperature of water. Sizing ensures your heat pump operates efficiently. An oversized unit can lead to short cycling, wasting energy.
The Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA) suggests a Manual J calculation for accurate sizing. This method considers home layout, insulation, and regional climate. For instance, a 2,000 square foot home in a colder area may need about 36,000 BTUs for heating. However, poorly insulated homes might require more. This nuance highlights the importance of precise calculations.
Homeowners often overlook factors like window size and orientation. These elements affect heat loss or gain. A south-facing window can increase heating needs in winter. Accurate sizing helps avoid discomfort and excessive utility bills. Always consult a professional for a thorough assessment. Mistakes in measurement can lead to costly inefficiencies. An informed choice can significantly enhance your home's energy performance.
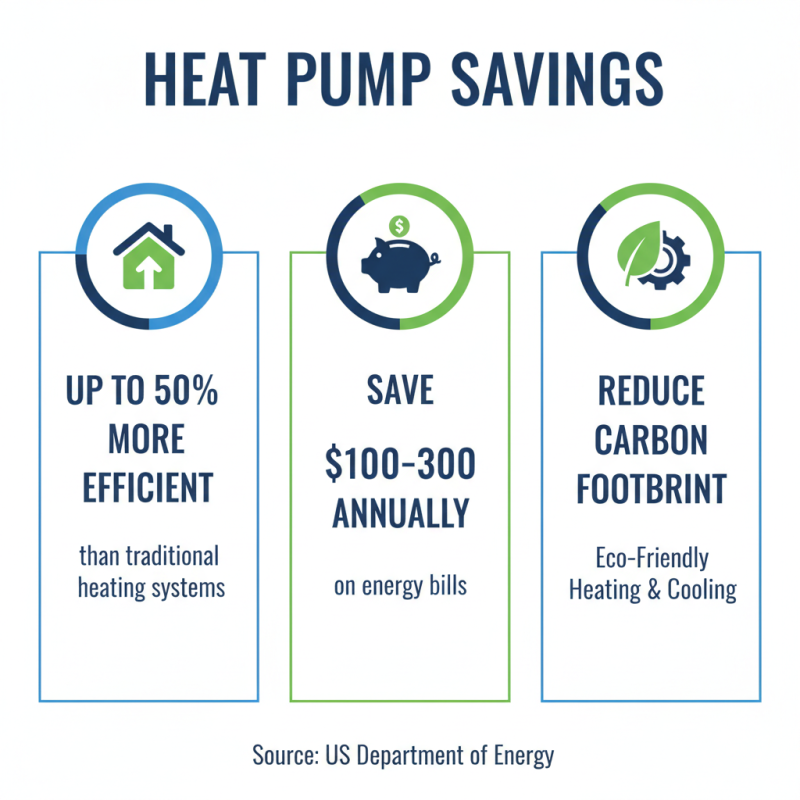
Choosing the right heat pump is crucial for both installation costs and long-term savings. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can be up to 50% more efficient than traditional heating systems. This efficiency translates to significant savings over time. For example, a properly installed heat pump can save homeowners $100 to $300 annually on energy bills.
When assessing installation costs, consider both initial and long-term investments. Installation costs for a heat pump typically range from $3,500 to $7,500. While this may seem high, the efficiency of heat pumps can lead to lower utility bills. A report from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory highlights that homeowners can recoup their installation costs within 5 to 10 years through energy savings.
Tips: Look for local incentives. Many regions offer rebates for energy-efficient systems, which can reduce upfront costs. Energy audits can help determine the right size and type of heat pump for your home’s specific needs. Always compare quotes from multiple contractors to ensure you make an informed decision.
Some homeowners may overlook maintenance costs. Regular servicing is essential to maintain efficiency. Neglecting this can lead to higher bills and reduced lifespan.






