Leave Your Message
When it comes to enhancing the energy efficiency of your home, selecting the best heat pump heater is crucial. According to industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading specialist in HVAC technologies, "A heat pump heater not only offers effective climate control but also plays a significant role in reducing energy costs over time." As homeowners increasingly seek sustainable and cost-effective heating solutions, understanding the key factors in choosing the right heat pump heater becomes essential.
In today's market, there are numerous models and technologies available, making the selection process overwhelming. Beyond cost considerations, homeowners must evaluate the energy efficiency ratings, the size of the unit in relation to their home, and additional features such as smart thermostats and zoning capabilities. Dr. Carter emphasizes that "the right heat pump heater can substantially decrease your environmental footprint while providing comfort." These considerations are critical for ensuring that the system you choose meets your unique heating needs while optimizing efficiency throughout the seasons.
Ultimately, making an informed decision about your home's heating system will not only improve comfort but also contribute to long-term savings. With the right guidance and knowledge about heat pump heaters, you can navigate this decision with confidence and select a solution that is both effective and environmentally friendly.


Heat pump heaters are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency and ability to provide both heating and cooling. Understanding the different types of heat pump heaters is essential for optimizing home efficiency. There are primarily three types of heat pumps: air-source, ground-source (geothermal), and water-source. Air-source heat pumps are the most common, extracting heat from the outside air, while ground-source heat pumps use the stable temperature of the ground, making them highly efficient in extreme weather conditions. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, air-source heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of 300-400%, meaning they can provide three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity used.
When choosing a heat pump heater, pay close attention to efficiency ratings. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) are critical indicators of performance. A higher SEER rating indicates better efficiency during cooling seasons, while a higher HSPF shows better performance during heating. Studies indicate that selecting units with a SEER of at least 16 and an HSPF of 9.0 or higher can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs over the lifetime of the unit.
Tips: Consider getting a professional energy audit for your home to assess the best type of heat pump for your needs. Additionally, ensure to check local energy incentives, as many utility companies offer rebates for efficient heating solutions. Regular maintenance and servicing can also help to improve your heat pump's efficiency and lifespan. Make sure to replace filters regularly to maintain optimal airflow and efficiency.
When selecting a heat pump heater for your home, understanding the key factors influencing its performance is crucial for achieving optimal energy efficiency.
One primary factor is the climate in which you live. Heat pumps operate by transferring heat from one location to another, and their effectiveness can vary significantly depending on ambient temperatures. In milder climates, heat pumps can efficiently heat and cool homes, but their performance may decline in extreme cold, necessitating a supplemental heating source.
Another essential consideration is the size of the heat pump relative to your home. An appropriately sized unit ensures efficient operation; too small a system will struggle to maintain desired temperatures, while an oversized unit may cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy and leading to uneven heating.
Additionally, proper installation plays a vital role in the system's effectiveness. Ensuring that the heat pump is installed correctly and that the home is well-insulated will maximize performance, reducing energy consumption and costs over time.
When evaluating heat pump heaters for home efficiency, understanding the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Season Performance Factor) ratings is crucial.
SEER measures the cooling efficiency of air-source heat pumps, indicating how much cooling output is generated per unit of energy consumed over a cooling season. A higher SEER rating signifies better energy efficiency, which not only results in lower utility bills but also reduces the environmental impact of energy consumption. It is essential to consider your local climate and cooling needs when selecting a unit with an appropriate SEER rating.
On the other hand, HSPF quantifies the heating efficiency during the heating season. Similar to the SEER rating, a higher HSPF indicates better performance, translating to increased energy savings and improved comfort during colder months. When comparing models, it is advisable to look for heat pumps with both high SEER and HSPF ratings, as they work together to provide balanced performance in varying temperatures.
Understanding the relationship between these ratings can help homeowners make informed decisions, ultimately leading to a more efficient and comfortable living environment.
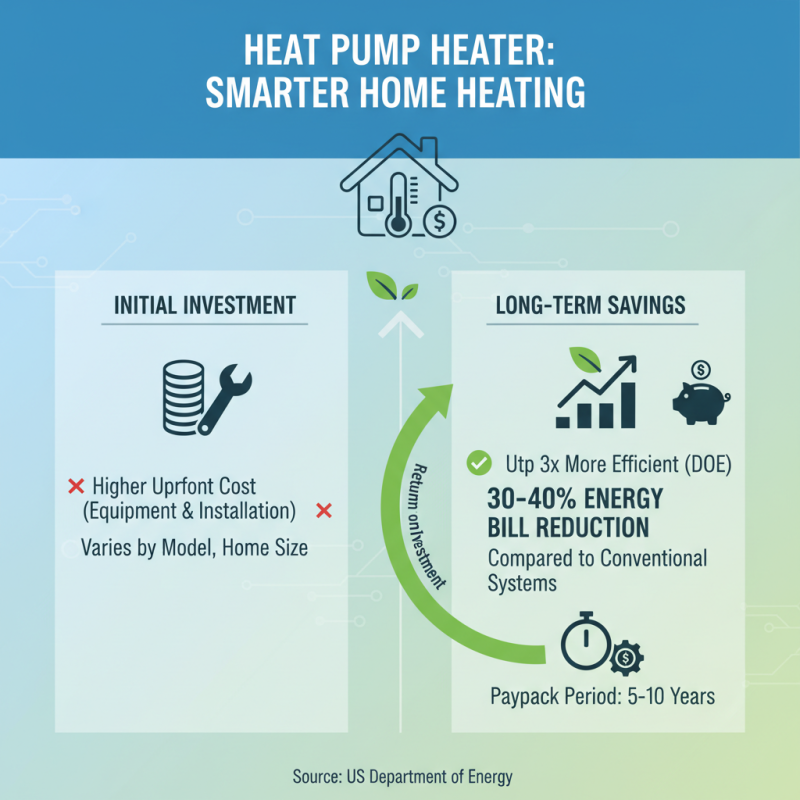
When considering the installation of a heat pump heater, a critical aspect to evaluate is the cost-benefit analysis of the initial investment compared to long-term savings. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can deliver up to three times more heating energy to a home than the electrical energy they consume. This significant efficiency translates into potential savings on energy bills, often ranging from 30% to 40% when compared to conventional heating systems.
However, the upfront costs of heat pump systems can be steeper, generally between $3,000 to $8,000, depending on the size and type. This initial investment might deter homeowners, but it's essential to consider the long-term savings. With an average lifespan of 15-20 years, the return on investment can be substantial, especially with rising utility costs. Homeowners may recoup their installation costs within 5 to 10 years through energy savings, making this a financially viable option in the long run.
**Tip:** To maximize savings, consider home energy audits to identify areas for improved efficiency prior to installation.
Taking into account local energy costs and climate conditions is crucial. Some regions may have incentives or rebates available, further reducing the initial expenditure.
**Tip:** Research local energy programs that offer financial assistance for energy-efficient upgrades, which can ease your upfront costs significantly.
Overall, weighing the initial expenditures against the potential for long-term savings is vital in choosing the best heat pump heater for your home efficiency.
When it comes to maximizing the efficiency of your heat pump heater, proper installation and maintenance are crucial. First and foremost, the heat pump should be installed by a qualified technician who understands the specific requirements of your home and the system. Ensuring that the heat pump is the right size for your space will prevent inefficiencies caused by oversizing or undersizing the unit. Additionally, it’s important to locate the outdoor unit in a place that allows for optimal airflow and avoids obstructions like debris or foliage that can hinder performance.
Once installed, regular maintenance will significantly enhance the efficiency and longevity of your heat pump heater. Start by regularly checking and cleaning or replacing the air filters, as clogged filters can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency. Furthermore, it’s advisable to schedule annual professional inspections that include checking the refrigerant levels, inspecting ductwork for leaks, and cleaning the coils.
Keeping these components in good working order will not only ensure efficient operation but also enhance indoor air quality and comfort.






